Session 05-07 - Function Determination & Funktionsscharen
Section 05: Differential Calculus
Entry Quiz - 10 Minutes
Quick Review from Session 05-06
Test your understanding of optimization and curve sketching
For \(f(x) = x^3 - 6x^2 + 9x\), find all critical points and classify them.
What is the difference between a local maximum and an absolute maximum?
Find the absolute extrema of \(g(x) = x^2 - 4x + 1\) on \([0, 3]\).
A profit function is \(P(x) = -2x^2 + 40x - 100\). What production level maximizes profit?
Homework Discussion - 15 Minutes
Your questions from Session 05-06
What questions do you have regarding the previous session?
Learning Objectives
What You’ll Master Today
- Set up systems of equations from function conditions
- Apply point conditions to determine unknown coefficients
- Use tangent/slope conditions with derivatives
- Incorporate extrema conditions (f’(a) = 0 and f(a) = b)
- Master Funktionsscharen (function families with parameters)
- Analyze how parameters affect zeros, extrema, and inflection points
- Apply systematic problem-solving to business scenarios
Funktionsscharen are heavily tested on exams! Both function determination and Funktionsscharen share a key skill: setting up equations from conditions systematically.
Part A: Point Conditions and System Setup
The General Approach
Strategy for Finding Unknown Functions:
- Choose the function form (polynomial degree, rational, etc.)
- Count unknowns (how many coefficients?)
- Identify conditions (points, slopes, extrema, etc.)
- Set up equations from conditions
- Solve the system
- Verify the solution
Number of conditions = Number of unknowns
For a function with \(n\) unknowns, you need exactly \(n\) independent conditions!
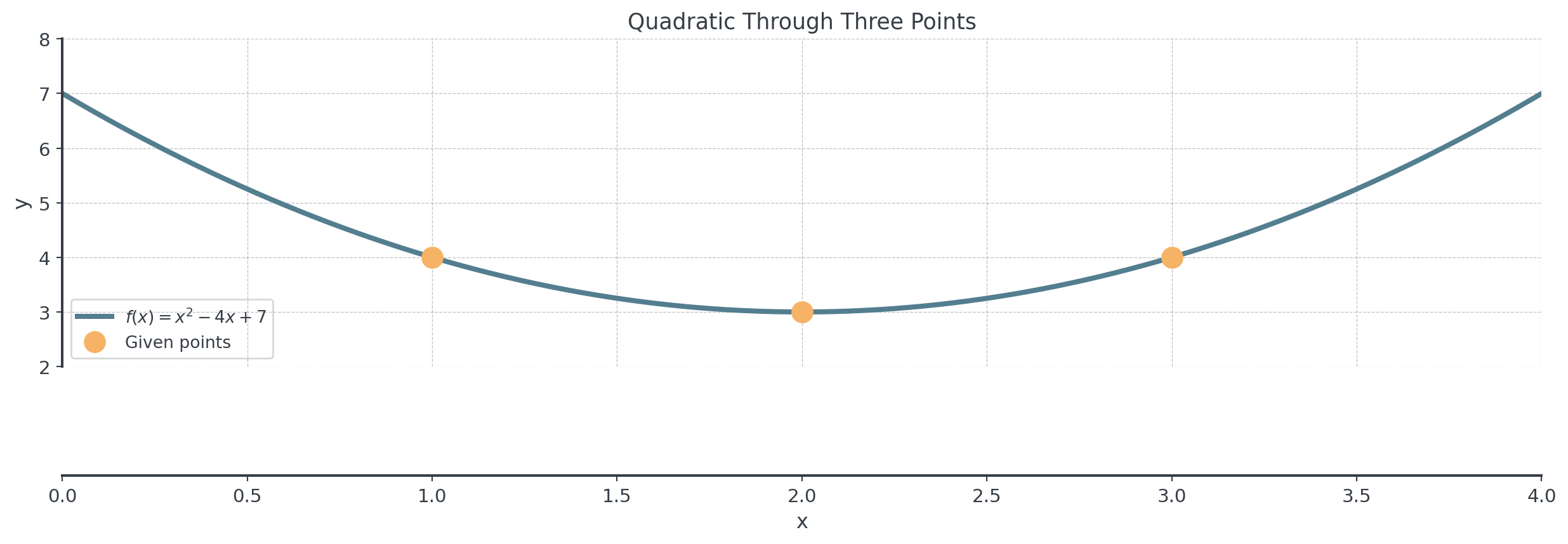
Example: Quadratic Three Points
Problem:
- Find the quadratic function \(f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\) passing through \((1, 4)\), \((2, 3)\), and \((3, 4)\).
Solution:
- Function form: \(f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\) (3 unknowns: \(a, b, c\))
- Three point conditions (need 3 equations)
- \(f(1) = 4: \quad a(1)^2 + b(1) + c = 4 \quad \implies \quad a + b + c = 4\)
- \(f(2) = 3: \quad a(4) + b(2) + c = 3 \quad \implies \quad 4a + 2b + c = 3\)
- \(f(3) = 4: \quad a(9) + b(3) + c = 4 \quad \implies \quad 9a + 3b + c = 4\)
Solving the System
System of equations:
\(\begin{cases} a + b + c = 4 \\ 4a + 2b + c = 3 \\ 9a + 3b + c = 4 \end{cases}\)
Answer: \(f(x) = x^2 - 4x + 7\)
Check: Does \(f(x) = x^2 - 4x + 7\) pass through all three points?
- \(f(1) = 1 - 4 + 7 = 4\) ✓
- \(f(2) = 4 - 8 + 7 = 3\) ✓
- \(f(3) = 9 - 12 + 7 = 4\) ✓
Visualizing the Solution
Part B: Tangent and Derivative Conditions
Using Derivative Conditions
Key Idea: Derivative conditions give us additional equations!
Common derivative conditions:
- Slope at a point: \(f'(a) = m\)
- “The tangent line at \(x = a\) has slope \(m\)”
- Horizontal tangent: \(f'(a) = 0\)
- “The function has a horizontal tangent at \(x = a\)”
- Parallel tangents: \(f'(a) = f'(b)\)
- “Slopes at two points are equal”
Remember: Each derivative condition counts as one equation!
Example 2: Quadratic Point and Slope
Problem:
- Find \(f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\) such that:
- Passes through \((1, 3)\)
- Has slope \(2\) at \(x = 1\)
- Passes through \((2, 5)\)
Solution:
Step 1: \(f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\) and \(f'(x) = 2ax + b\) (3 unknowns)
Solving with Derivative Conditions
Step 2: Set up equations from conditions:
- Point \((1, 3)\): \(a + b + c = 3\)
- Slope at \(x=1\): \(f'(1) = 2a + b = 2\)
- Point \((2, 5)\): \(4a + 2b + c = 5\)
System: \(\begin{cases} a + b + c = 3 \\ 2a + b = 2 \\ 4a + 2b + c = 5 \end{cases}\)
Answer: \(f(x) = 2x + 1\) (actually linear, not quadratic!)
Part C: Extrema Conditions
Extrema Give TWO Conditions
Important: When a function has an extremum (max or min) at \((a, b)\):
You get TWO conditions:
- Point condition: \(f(a) = b\) (the function passes through the point)
- Horizontal tangent: \(f'(a) = 0\) (slope is zero at extremum)
Total: 2 equations from one extremum condition!
Don’t forget the \(f'(a) = 0\) condition!
An extremum at \((a, b)\) gives you both the point and the derivative condition.
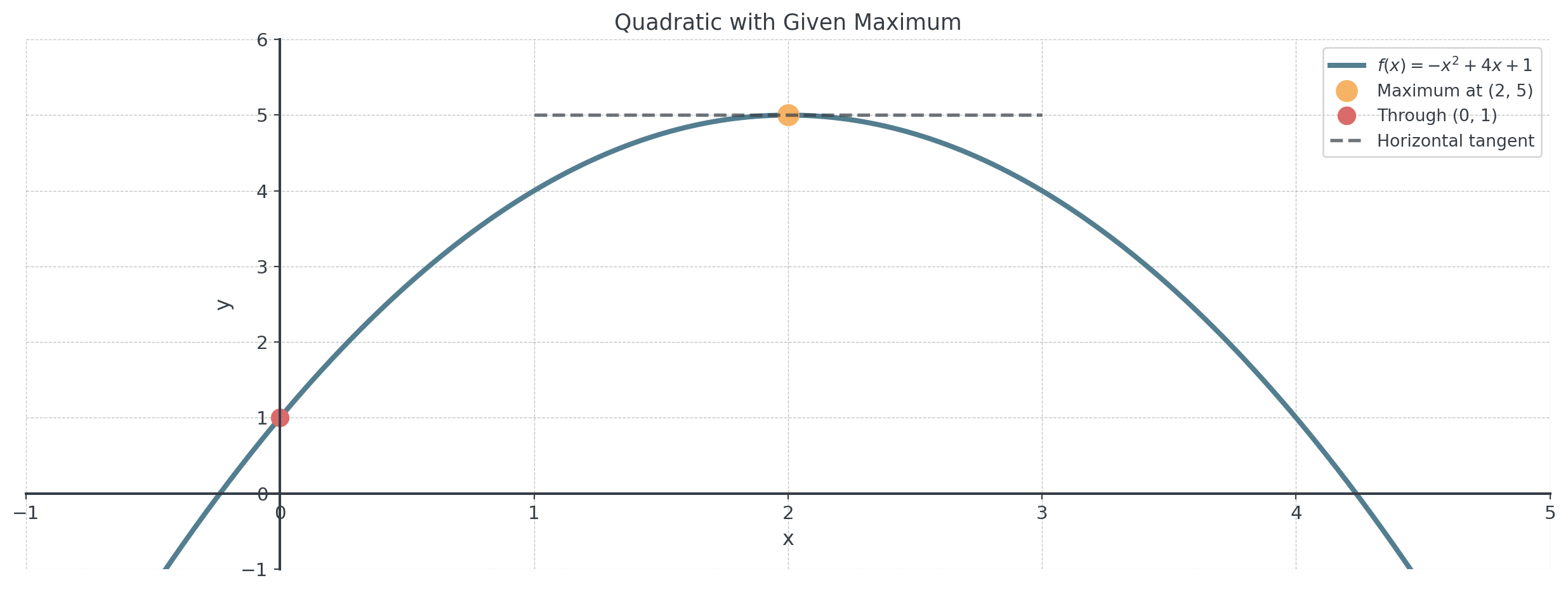
Example 3: Quadratic with Maximum
Problem: Find the quadratic function with a maximum at \((2, 5)\) that passes through \((0, 1)\).
Solution:
\(f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\) (3 unknowns)
Conditions:
- Point \((0, 1)\): \(f(0) = 1\)
- Maximum at \((2, 5)\): \(f(2) = 5\)
- Horizontal tangent at max: \(f'(2) = 0\)
Solving the Extremum System
Important: \(f'(x) = 2ax + b\)
Equations:
\(\begin{cases} c = 1 & \text{from } f(0) = 1 \\ 4a + 2b + c = 5 & \text{from } f(2) = 5 \\ 4a + b = 0 & \text{from } f'(2) = 0 \end{cases}\)
Answer: \(f(x) = -x^2 + 4x + 1\)
Verification: \(f''(x) = -2 < 0\) confirms maximum ✓
Visualizing the Maximum
Example 4: Parabola with Vertex Form
Problem: Find the parabola with vertex at \((3, -2)\) passing through \((1, 6)\).
Two approaches:
- Approach 1 - Standard form: \(f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\) (harder)
- Approach 2 - Vertex: \(f(x) = a(x - h)^2 + k\) where \((h, k)\) vertex
Now it’s easy!
- Using vertex form with \((h, k) = (3, -2)\):
- \(f(x) = a(x - 3)^2 - 2\)
- Only 1 unknown (\(a\)) now!
Vertex Simplification
Condition: Passes through \((1, 6)\):
- \(f(1) = a(1 - 3)^2 - 2 = 6\)
- \(4a - 2 = 6\)
- \(a = 2\)
Answer:
- \(f(x) = 2(x - 3)^2 - 2\)
- Expanded: \(f(x) = 2x^2 - 12x + 16\)
Break - 10 Minutes
Part D: Mixed Conditions and Function Families
Multiple Conditions I
Strategy for Complex Problems:
- List all unknowns clearly
- Identify each condition type:
- Point: \(f(a) = b\)
- Slope: \(f'(a) = m\)
- Extremum: \(f(a) = b\) AND \(f'(a) = 0\)
- Inflection: \(f''(a) = 0\) (and possibly \(f(a) = b\))
Remember that the number of unknowns must match the number of conditions!
Multiple Conditions II
Strategy for Complex Problems:
- Write derivative(s) before setting up equations
- Organize your system (group similar types)
- Solve systematically (substitution or elimination)
- Verify your answer
Not too complicated, right?
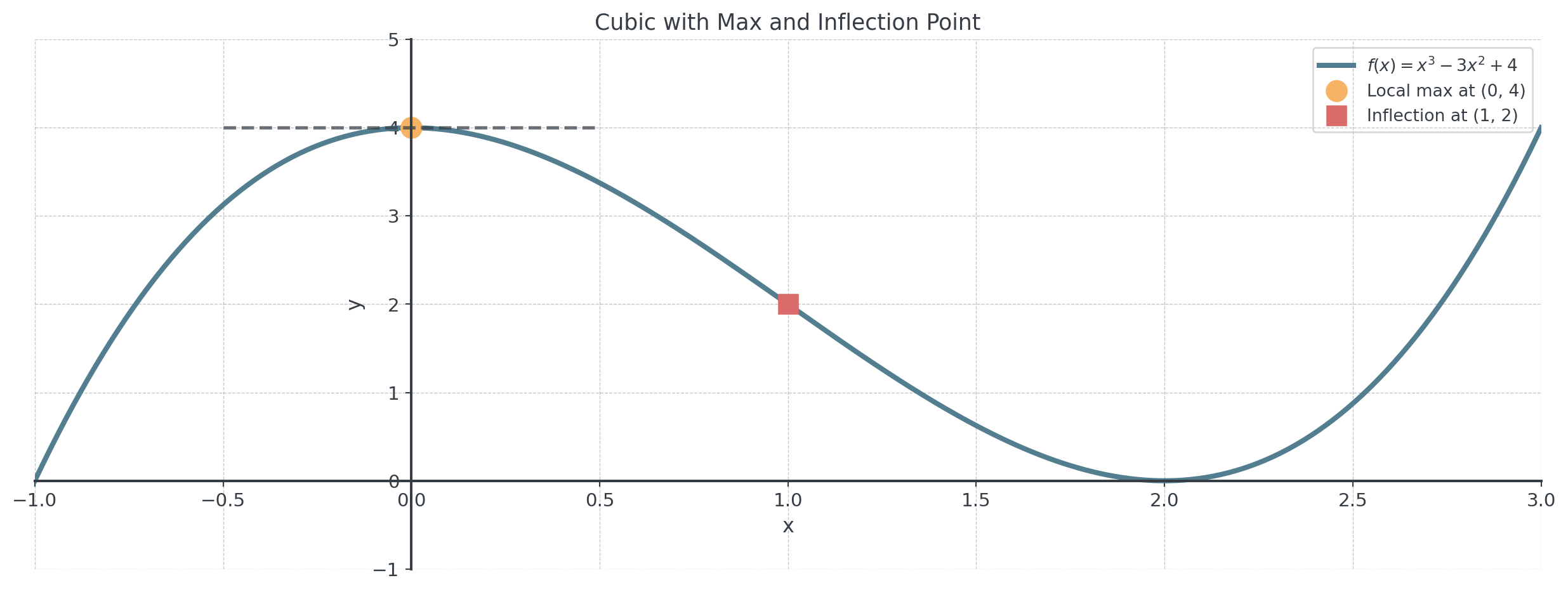
Example 5: Cubic Mixed Conditions
Problem: Find \(f(x) = ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d\) such that:
- Has a local maximum at \((0, 4)\)
- Has an inflection point at \((1, 2)\)
Analysis: 4 unknowns, need 4 equations
- Derivatives:
- \(f'(x) = 3ax^2 + 2bx + c\)
- \(f''(x) = 6ax + 2b\)
The Conditions
Now, remember the conditions we have:
- \(f(0) = 4\): point condition
- \(f'(0) = 0\): horizontal tangent at max
- \(f(1) = 2\): point condition at inflection
- \(f''(1) = 0\): inflection point condition
You will need to know these by heart in the exam!
Solving the Equations
Problem: Find \(f(x) = ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d\) such that:
- Has a local maximum at \((0, 4)\)
- Has an inflection point at \((1, 2)\)
Equations:
- \(f(0) = 4\): \(d = 4\)
- \(f'(0) = 0\): \(c = 0\)
- \(f(1) = 2\): \(a + b + c + d = 2\), so \(a + b = -2\)
- \(f''(1) = 0\): \(6a + 2b = 0\), so \(3a + b = 0\)
Verification
Answer: \(f(x) = x^3 - 3x^2 + 4\)
Check all conditions for \(f(x) = x^3 - 3x^2 + 4\):
- \(f(0) = 4\) ✓
- \(f'(x) = 3x^2 - 6x\), so \(f'(0) = 0\) ✓
- \(f(1) = 1 - 3 + 4 = 2\) ✓
- \(f''(x) = 6x - 6\), so \(f''(1) = 0\) ✓
Additional check: \(f''(0) = -6 < 0\), confirming local maximum ✓
Visualizing Mixed Conditions
Part E: Funktionsscharen (Function Families)
Introduction to Funktionsscharen
Definition: A Funktionenschar is a family of functions that depend on a parameter we can vary (usually \(t\), \(a\), or \(k\)).
- Notation: \(f_t(x)\) or \(f(x, t)\)
- Example: \(f_t(x) = x^2 - tx + 1\)
- When \(t = 0\): \(f_0(x) = x^2 + 1\)
- When \(t = 2\): \(f_2(x) = x^2 - 2x + 1 = (x-1)^2\)
- When \(t = 4\): \(f_4(x) = x^2 - 4x + 1\)
- Each value of \(t\) gives a different parabola!
Visualizing a Function Family
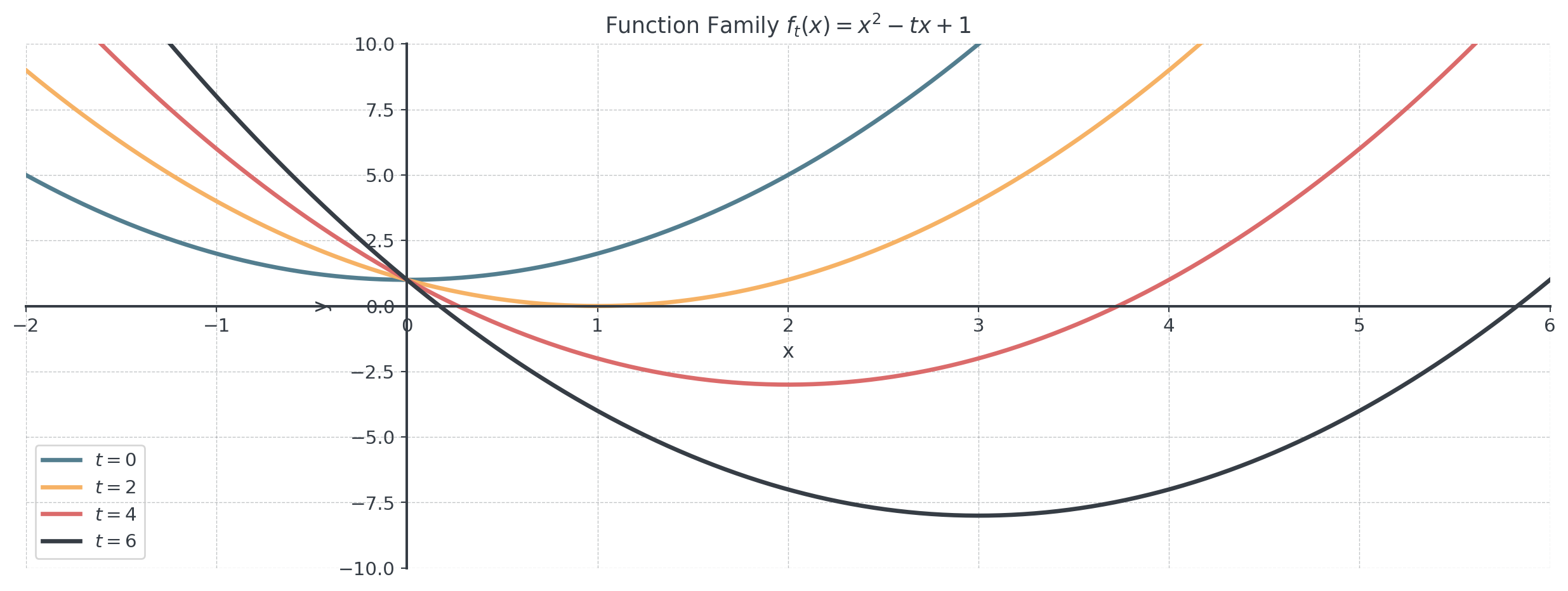
Its a collection of functions that are related to each other by a parameter.
Why Study Funktionsscharen?
Heavily tested on exams! Common question types:
- For which \(t\) does \(f_t(x)\) have exactly 2 zeros?
- For which \(t\) does \(f_t(x)\) have a local maximum at \(x = 3\)?
- For which \(t\) is \(f_t(2) = 5\)?
- Find the parameter \(t\) such that the inflection point is at \(x = 1\).
Practice these on your own as well, as we are coming to the end of this section!
Example
Problem: For which \(t\) does \(f_t(x) = x^2 - tx + t\) have exactly one zero?
- Solution: Exactly one zero when the discriminant equals zero.
- For \(x^2 - tx + t = 0\):
- \(\Delta = b^2 - 4ac = (-t)^2 - 4(1)(t) = t^2 - 4t\)
- Set \(\Delta = 0\):
- \(t^2 - 4t = 0\)
- \(t(t - 4) = 0\)
- \(t = 0 \text{ or } t = 4\)
- Answer: For \(t = 0\) or \(t = 4\), the function has exactly one zero.
General Strategy for Funktionsscharen
- Identify condition: zeros, extrema, inflection points, function values
- Set up the equation:
- Zeros: Use discriminant or factor
- Extrema: \(f_t'(x) = 0\)
- Inflection: \(f_t''(x) = 0\)
- Function value: \(f_t(a) = c\)
- Substitute the given point (if specified)
- Solve for the parameter \(t\)
- Verify your answer makes sense
Guided Practice - 15 Minutes
Set A - Work in Pairs
Complete these problemsand then we discuss
- Find the quadratic passing through \((1, 0)\), \((2, 3)\), and \((3, 8)\).
- Find the cubic \(f(x) = ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d\) with \(f(0) = 2\), \(f(1) = 3\), \(f'(0) = 1\), and \(f'(1) = 4\).
- Find the parabola with vertex at \((2, -1)\) passing through \((0, 7)\).
- For \(h_t(x) = x^2 - tx + 3\), find \(t\) such that \(h_t(2) = 5\).
Set B - Funktionsscharen Practice
Work individually for 10 minutes, then compare
For each Funktionschar, solve the given problem:
For \(f_t(x) = x^2 - 2tx + 3\), find all \(t\) such that \(f_t\) has exactly two zeros.
For \(g_t(x) = tx^2 - 4x + t\), find \(t\) such that \(g_t\) has a zero at \(x = 2\).
For \(h_t(x) = x^3 - tx^2 + 3x\), find \(t\) such that \(h_t\) has a local extremum at \(x = 1\).
For \(p_t(x) = x^2 + tx - 2t\), find \(t\) such that \(p_t(3) = 10\).
For \(q_t(x) = tx^2 - 6x + 9\), for which \(t\) does \(q_t\) have exactly one zero?
Coffee Break - 15 Minutes
Business Applications
Cost Function from Marginal Cost
Scenario: A company knows its marginal cost is:
\[MC(x) = C'(x) = 3x^2 - 12x + 20\]
The fixed cost (when \(x = 0\)) is €500.
Question: Find the total cost function \(C(x)\).
Solution: We need to find \(C(x)\) such that \(C'(x) = 3x^2 - 12x + 20\).
Integration
Integration (reverse of differentiation):
\[C(x) = x^3 - 6x^2 + 20x + k\]
where \(k\) is a constant.
Use the fixed cost condition \(C(0) = 500\):
\[C(0) = 0 - 0 + 0 + k = 500\]
\[k = 500\]
Answer: \(C(x) = x^3 - 6x^2 + 20x + 500\)
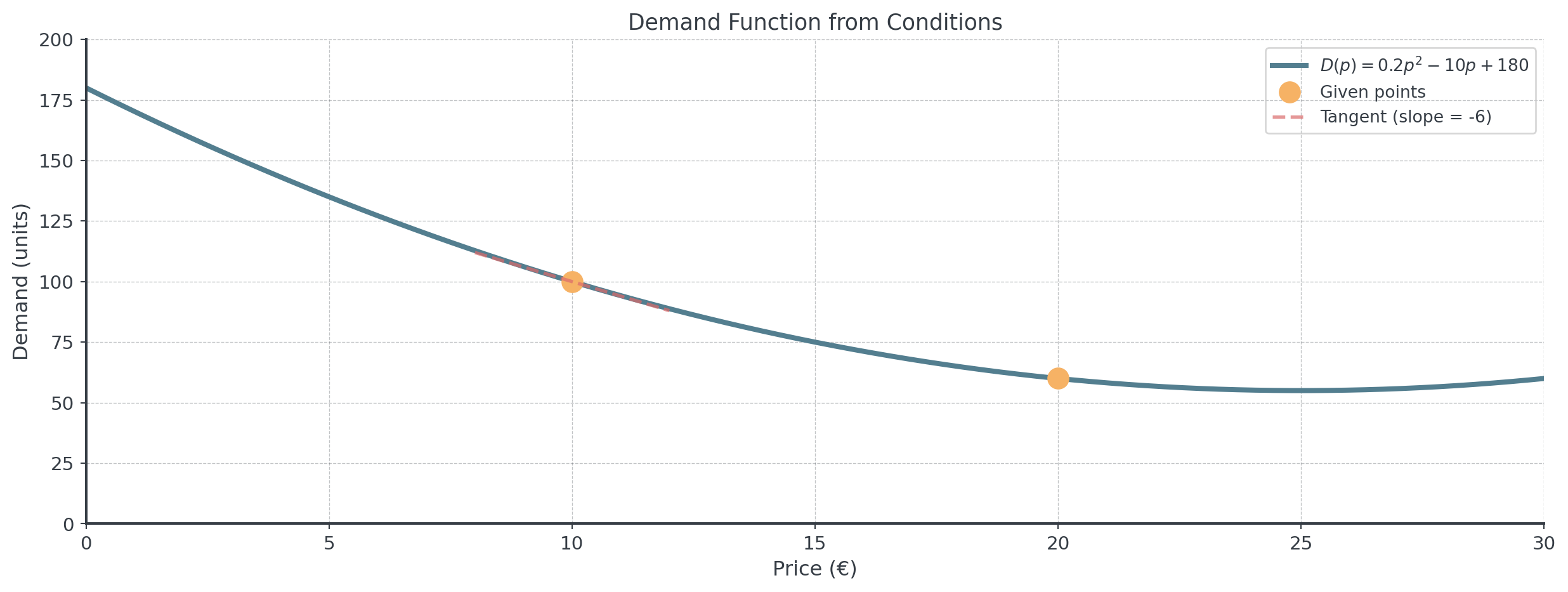
Demand Function Determination
Scenario: A product’s demand function is quadratic: \(D(p) = ap^2 + bp + c\) where \(p\) is price.
Known information:
- At price €10, demand is 100 units: \(D(10) = 100\)
- At price €20, demand is 60 units: \(D(20) = 60\)
- The rate of change of demand at \(p = 10\) is \(-6\) units/euro
- \(D'(10) = -6\)
Question: Find the demand function.
Solving the Demand System
\(D'(p) = 2ap + b\)
System: \[\begin{cases} 100a + 10b + c = 100 \\ 400a + 20b + c = 60 \\ 20a + b = -6 \end{cases}\]
Answer: \(D(p) = 0.2p^2 - 10p + 180\)
Visualizing the Demand Function
Collaborative Problem-Solving - 20 Minutes
Group Challenge I
Scenario:
An engineer is designing a roller coaster section modeled by a cubic function \(h(x) = ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d\), where \(h\) is height (meters) and \(x\) is horizontal distance (meters).
Design requirements:
- Starts at ground level: \(h(0) = 0\)
- Reaches a peak (maximum) of 20 meters at \(x = 4\)
- Returns to ground level at \(x = 10\): \(h(10) = 0\)
Group Challenge II
Work in groups of 3-4 students
- How many unknowns and conditions do you have?
- Set up the complete system of equations.
- Solve for the coefficients \(a, b, c, d\).
- Verify that \(x = 4\) is indeed a maximum (not minimum).
- Find the height at \(x = 2\) and \(x = 8\).
- Sketch the roller coaster section.
Wrap-Up & Key Takeaways
Summary of Session 05-07
Function Determination - Systematic Approach:
- Count unknowns = count conditions needed
- Write derivatives before setting up equations
- Organize conditions by type: point, slope, extremum, inflection
Funktionsscharen - Parameter Analysis:
- Identify the parameter (usually \(t\), \(a\), or \(k\))
- Set up condition equations involving the parameter
- Solve for parameter values meeting given criteria
Final Assessment - 5 Minutes
Quick Check
Complete individually and then discuss
- How many conditions do you need to find a cubic function? How many does an extremum at \((a, b)\) provide?
- Find the parabola with vertex at \((1, 4)\) passing through \((0, 2)\).
- For \(f_t(x) = x^2 - 2tx + t\), find \(t\) such that \(f_t(x)\) has exactly one zero.
- Find the quadratic \(g(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\) with \(g(0) = 3\), \(g(1) = 2\), and \(g'(1) = -4\).
Next Session Preview
Looking Ahead: Session 05-08
Topic: First Complete Assessment (Full Mock Exam)
- 180-minute mock exam under exam conditions
- 3 complete multi-part problems
- Coverage: All differential calculus topics
- Exact exam conditions, no assistance
- Review of solutions after completion
- Bring calculator
Get a good night’s sleep!
Thank You!
See you next session!
Session 05-07 - Function Determination & Funktionsscharen | Dr. Nikolai Heinrichs & Dr. Tobias Vlćek | Home