Session 04-02 - Power Functions & Roots
Section 04: Advanced Functions
Entry Quiz - 10 Minutes
Review from Session 04-01
Work individually for 5 minutes, then we discuss
Determine the end behavior of \(P(x) = -3x^4 + 2x^2 - 7\)
Given \(Q(x) = 2(x - 1)^3(x + 2)\), identify all zeros and their multiplicities and describe what they mean
If a polynomial has degree 5, what is the maximal number of turning points it can have?
Sketch \((x - 2)(x + 1)^2\) on a number line
Homework Discussion - 15 Minutes
Your questions from Tasks 04-01
Focus on polynomial applications and factoring
- Challenges with the Rational Root Theorem
- Sketching polynomials from factored form
- Interpreting multiplicity in graphs
- Business context questions
Power functions will help us understand the individual components of polynomials!
Learning Objectives
Today’s Goals
By the end of this session, you will be able to:
- Understand power functions with integer, fractional, and negative exponents
- Determine domains of root functions and fractional powers
- Sketch power function graphs without a calculator
- Compare growth rates of different power functions
- Apply power functions to economic models
Power Functions with Integer Exponents
Definition and Basic Forms
The building blocks of polynomials
A power function has the form: \[f(x) = ax^n\]
where \(a \neq 0\) is a constant and \(n\) is a real number
- Integer powers: \(x^2, x^3, x^{-1}, x^{-2}\)
- Root functions: \(\sqrt{x}, \sqrt[3]{x}\)
- Fractional powers: \(x^{2/3}, x^{3/2}\)
Power functions are simpler than polynomials! But they reveal fundamental behaviors that help us understand all functions.
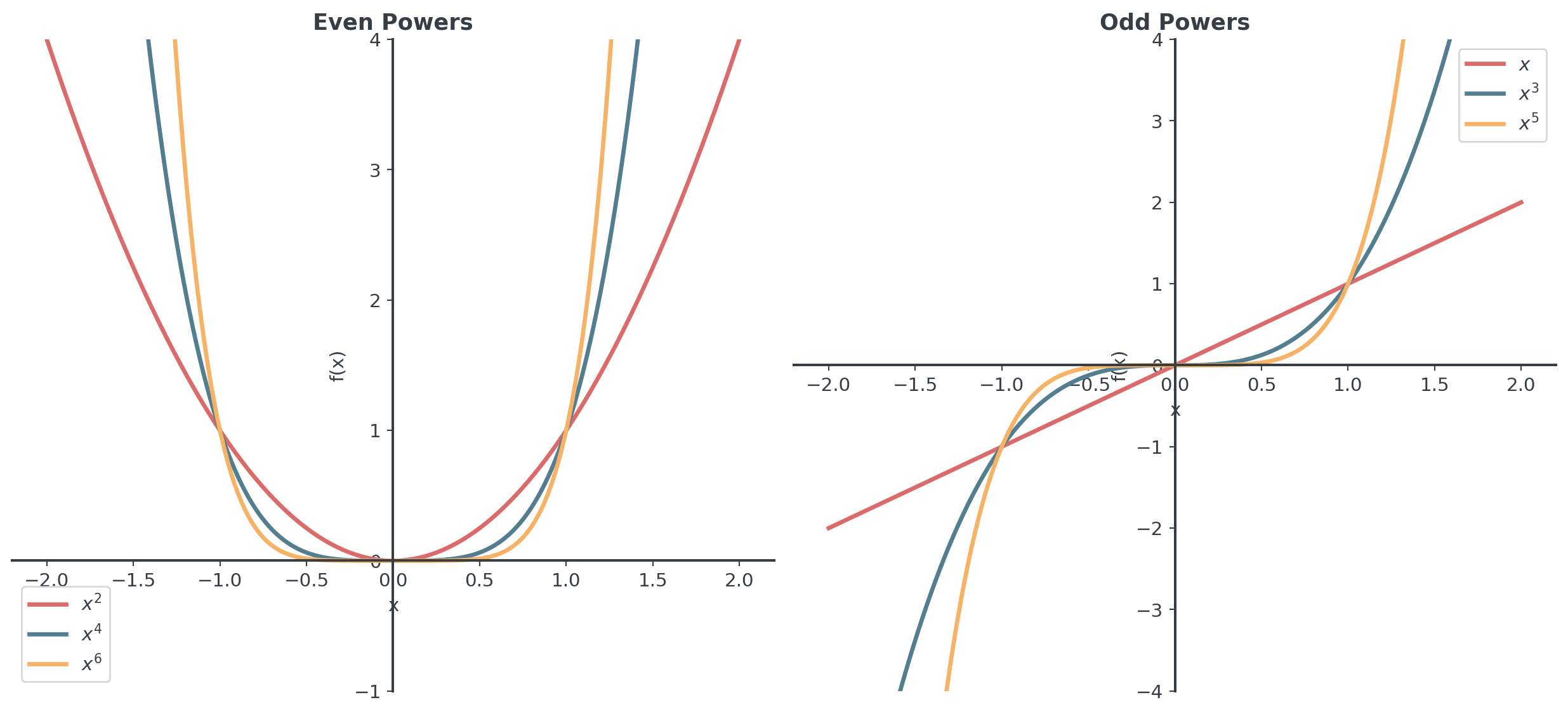
Comparing even and odd powers
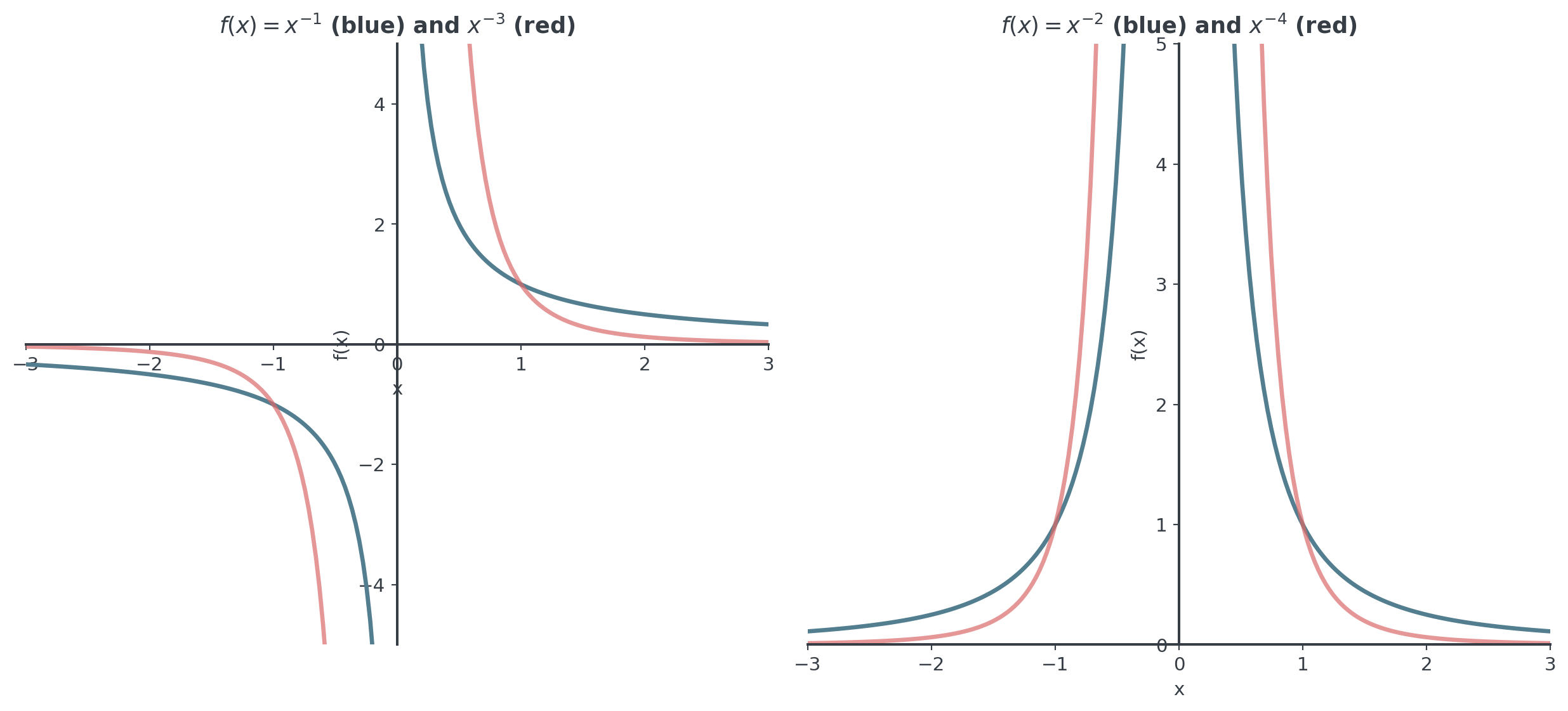
Negative Integer Powers (Reciprocal)
For \(n > 0\): \(f(x) = x^{-n} = \frac{1}{x^n}\), not defined at \(x = 0\)
Think-Pair-Share
2 minutes individual, 3 minutes pairs, 2 minutes class discussion
Compare and contrast:
- \(f(x) = x^2\) and \(g(x) = x^{-2}\)
- \(f(x) = x^3\) and \(g(x) = x^{-3}\)
Consider:
- Domain and range
- Symmetry
- Behavior near \(x = 0\)
- Behavior as \(x \to \pm\infty\)
Discussion Points
- Positive powers have \(x = 0\) in domain; negative powers don’t
- Both maintain same type of symmetry (even/odd)
- Reciprocal relationship: large becomes small, small becomes large
- Asymptotic behavior reverses
Root Functions
Functions with fractional exponents
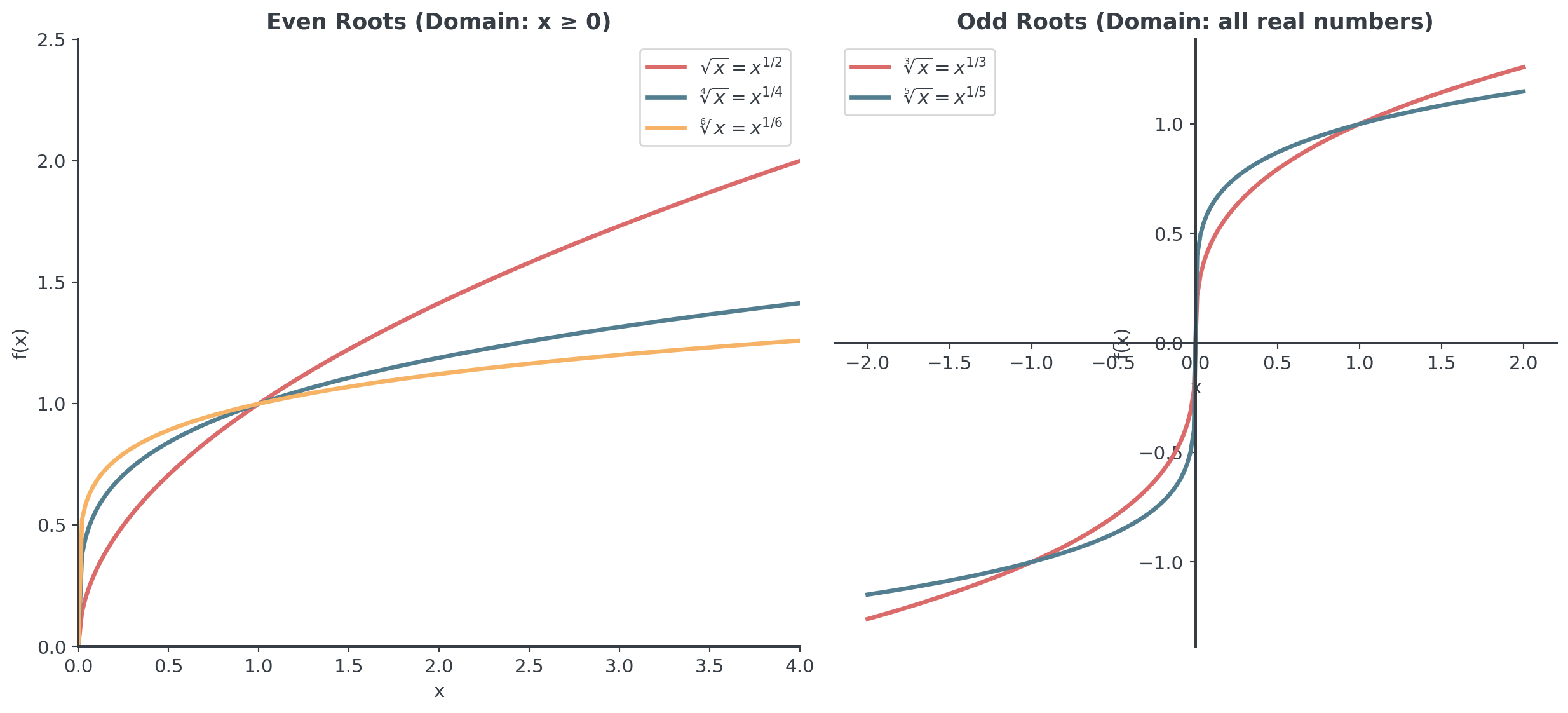
Domain Restrictions
Critical concept for root functions
like \(\sqrt{x}\), \(\sqrt[4]{x}\):
- Domain: \(x \geq 0\) only
- Why? Even roots of negative numbers aren’t real
- \(\sqrt{x^2} = |x|\) (always non-negative)
- Range: \(y \geq 0\)
like \(\sqrt[3]{x}\), \(\sqrt[5]{x}\):
- Domain: all real numbers
- Can take cube root of negative numbers
- Range: all real numbers
Fractional Powers
General Fractional Exponents
Combining powers and roots
For \(f(x) = x^{m/n}\) where \(m, n\) are integers, \(n > 0\):
\[x^{m/n} = (x^{1/n})^m = \sqrt[n]{x^m}\]
Domain depends on \(n\):
- If \(n\) is odd: all real numbers (usually)
- If \(n\) is even: \(x \geq 0\) required
Example: \(f(x) = x^{3/2} = \sqrt{x^3} = (\sqrt{x})^3\)
- Domain: \(x \geq 0\) (because of square root), grows faster than \(\sqrt{x}\) but slower than \(x^2\)
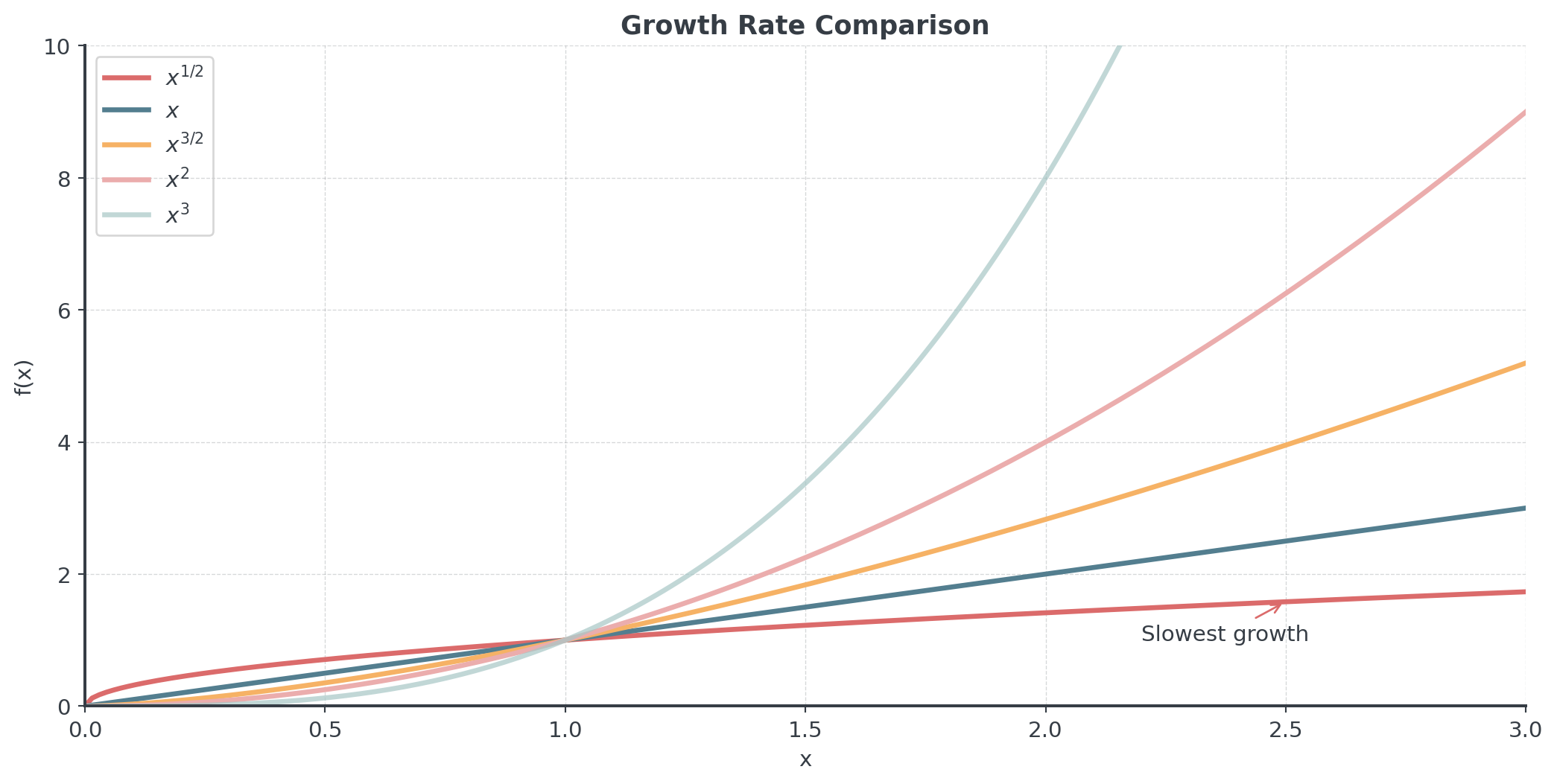
Comparing Growth Rates
Break - 10 Minutes
Economic Applications
Economies of Scale
Cost functions with fractional powers
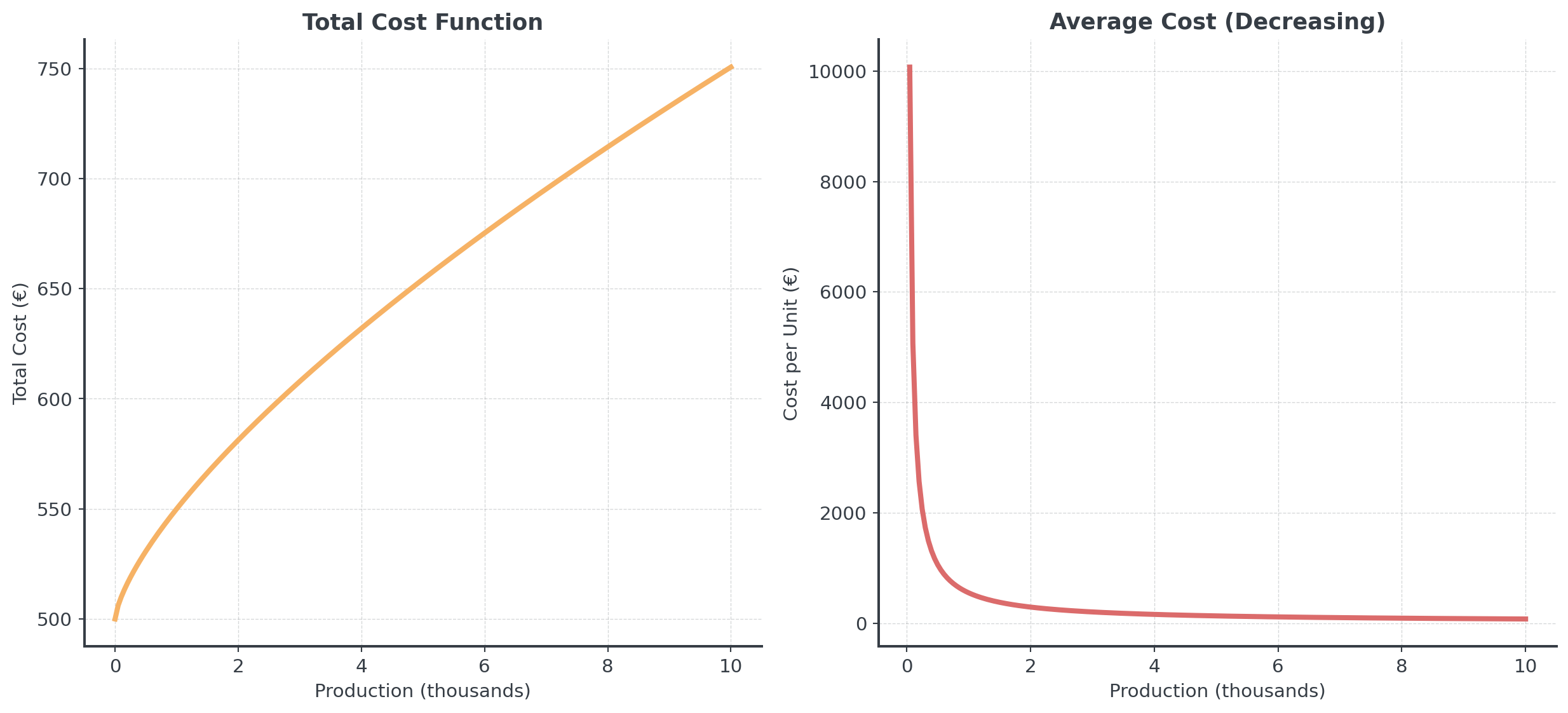
Many production processes exhibit economies of scale:
\[C(x) = 500 + 50x^{0.7}\]
where \(x\) is production quantity (thousands)
Question: Any idea why \(x^{0.7}\)?
Exponent < 1 means cost grows slower than production!
Economies of Scale II
Allometric Growth I
Biological and economic scaling
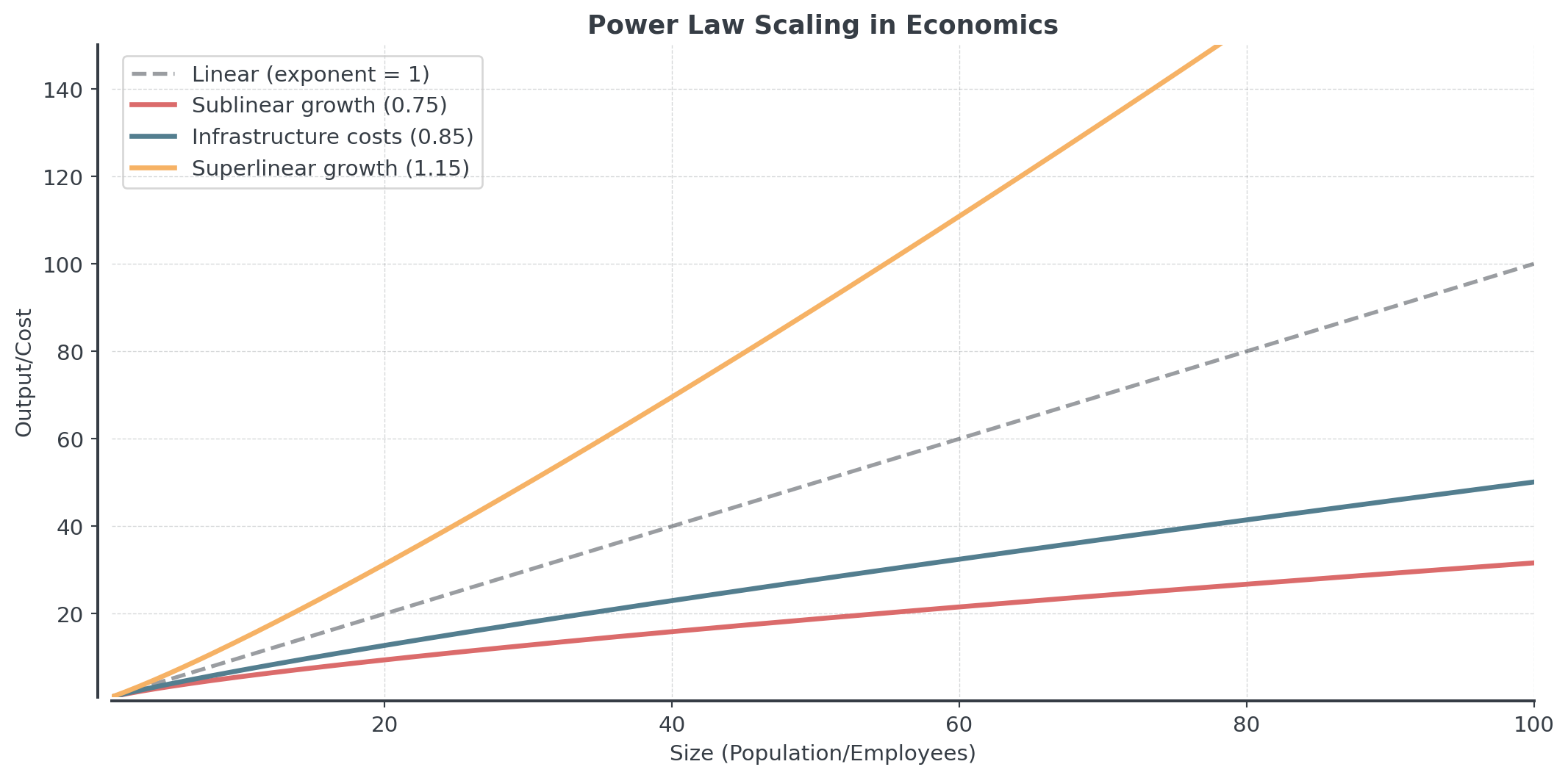
Many relationships follow power laws:
- Biology: Brain mass ∝ (Body mass)\(^{0.75}\)
- Economics:
- City infrastructure costs ∝ (Population)\(^{0.85}\)
- Company revenue ∝ (Number of employees)\(^{1.15}\)
Have you ever seen ∝ before? That’s the proportionality symbol (∝), which means “is proportional to” in mathematics.
Allometric Growth II
Surface Area and Volume
Geometric Power Relationships
Why packaging costs don’t scale linearly
Example: Doubling box dimensions
- Surface area increases by factor of \(2^2 = 4\)
- Volume increases by factor of \(2^3 = 8\)
- Material cost (surface) vs. capacity (volume)
This explains why larger packages have lower cost per unit volume. The discount has a mathematical basis!
Graphing Techniques
Sketching Power Functions
A systematic approach
Steps to sketch \(f(x) = ax^n\) or \(f(x) = ax^{m/n}\):
Determine domain
- Negative exponents: exclude \(x = 0\)
- Even roots: require \(x \geq 0\)
Find key points
- Always passes through \((1, a)\) if in domain
- Check \((0, 0)\) if applicable
Analyze end behavior
- Positive exponents: consider even/odd
- Negative exponents: approach axes
Check symmetry
- Even exponents: y-axis symmetry
- Odd exponents: origin symmetry
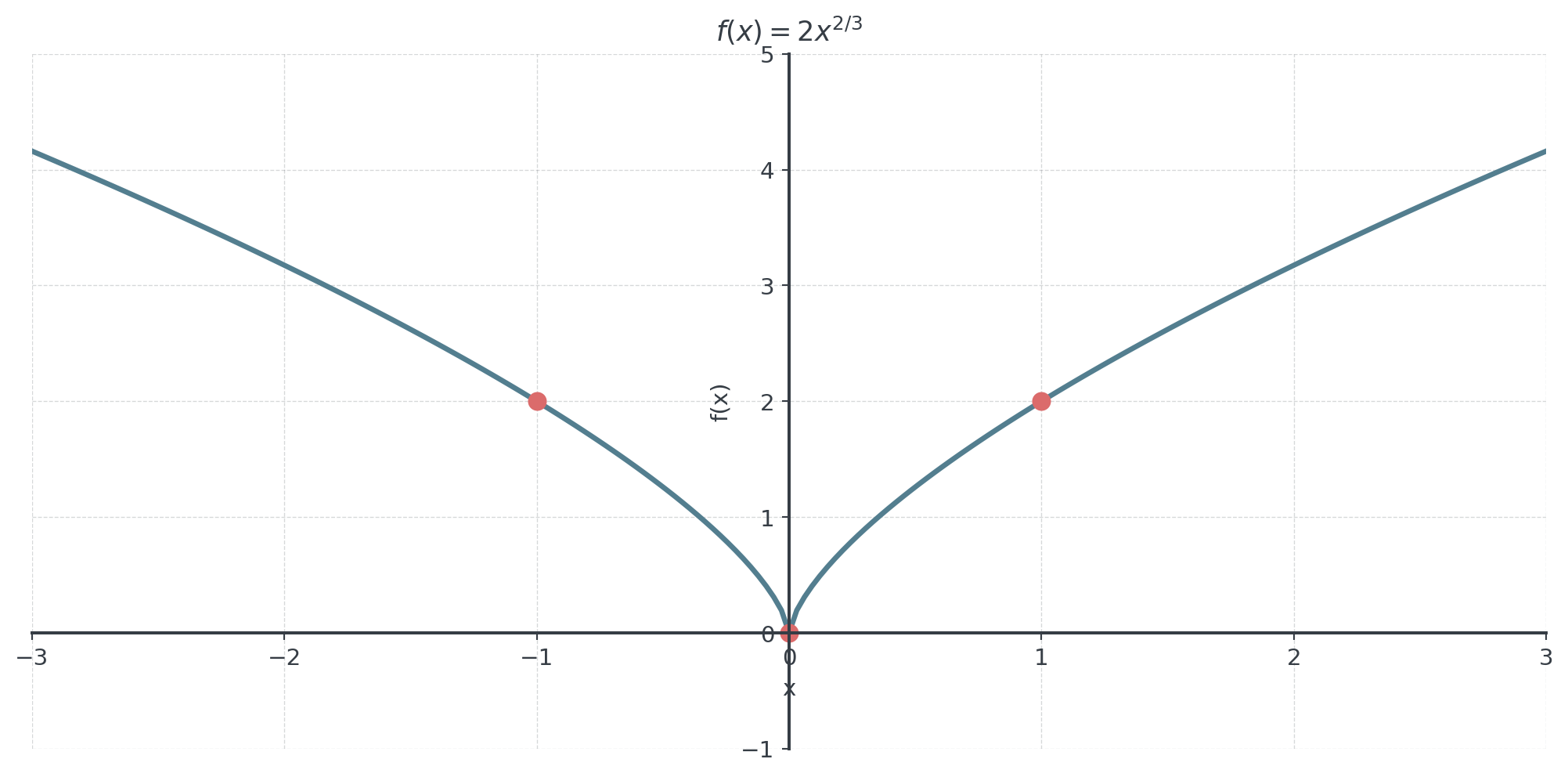
Practice: Sketch Without Calculator
Work together
Sketch: \(f(x) = 2x^{2/3}\)
Practice Domain and Range Analysis
Work together and discuss
For each function, determine the domain and range, then sketch a rough graph:
\(f(x) = 3x^{1/4}\)
\(g(x) = -2x^{-1}\)
\(h(x) = x^{3/5}\)
\(p(x) = 4 - x^{1/2}\)
Coffee Break - 15 Minutes
Combining Power Functions
Sums and Products
Building complex models
Real-world phenomena often combine power functions:
Total Cost with Multiple Effects:
\[C(x) = 1000x^{0.5} + 50x + 0.1x^2\]
- \(x^{0.5}\): Setup costs (economies of scale)
- \(x\): Linear variable costs
- \(x^2\): Capacity constraints (diseconomies)
Guided Practice - 25 Minutes
Individual Exercise Block I
Work alone for 5 minutes, then discuss for 5 minutes
Problem 1: A company’s profit function combines multiple effects: \[P(x) = -2x^3 + 15x^2 + 100\sqrt{x} - 500\]
where \(x\) is production level (hundreds of units), \(x > 0\)
- Identify each term’s economic interpretation
- Calculate \(P(4)\) and \(P(9)\)
- Which term dominates for large \(x\)? What does this tell management?
Individual Exercise Block II
Work alone for 5 minutes, then discuss for 5 minutes
Problem 2: Compare growth rates for large values:
- Which grows faster: \(f(x) = x^{1/2}\) or \(g(x) = x^{1/3}\)?
- Which grows faster: \(f(x) = x^{3/2}\) or \(g(x) = x^2\)?
- Order from slowest to fastest growth: \(x^{1/2}, x, x^{3/2}, x^2\)
Individual Exercise Block III
Work alone for 5 minutes, then discuss for 5 minutes
Problem 3: A technology company’s average cost per unit is: \[AC(x) = \frac{50000}{x} + 100 + 0.01x\]
where \(x\) is units produced.
- Identify the power function in each term
- What happens to average cost as \(x \to 0^+\)?
- What happens to average cost as \(x \to \infty\)?
- Graph the behavior conceptually
Spot the Error
Can you find what’s wrong? Work with your neighbor
Time allocation: 5 minutes to find errors, 5 minutes to discuss
Student work:
“\(\sqrt{x^2} = x\) for all \(x\)”
“The function \(f(x) = x^{-1/2}\) has domain \(x > 0\)”
“Since \(x^{2/3} = \sqrt[3]{x^2}\), the domain is \(x \geq 0\)”
“\(x^{1.5}\) grows faster than \(x^2\) because 1.5 is complicated”
Not everything has to be wrong!
Wrap-Up
Key Takeaways
Today’s essential concepts
- Power functions are the building blocks of polynomials
- Domain restrictions come from mathematical necessity
- Growth rate comparisons guide long-term planning
- Fractional powers create realistic economic models
Final Assessment
5 minutes - Individual work
A manufacturing company’s cost per unit follows: \[C(x) = 10000x^{-0.5} + 50 + 2x^{0.5}\]
where \(x\) is the number of units produced (in thousands).
What is the domain of this function in the business context?
Identify each term’s economic meaning
What happens to cost per unit as production increases dramatically?
Which term represents economies of scale?
Next Session Preview
Session 04-03: Exponential Functions
Moving from power to exponential growth
- Exponential growth and decay fundamentals
- The natural exponential \(e^x\) and its properties
- Compound interest and continuous growth
- Population models and doubling time
- Exponential vs. power function growth (critical comparison!)
- Half-life and decay applications
Complete Tasks 04-02!
Thank You!
Appendix: Sketch without calculator
Session 04-02 - Power Functions & Roots | Dr. Nikolai Heinrichs & Dr. Tobias Vlćek | Home